On the effect of age on the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in households, schools and the community | The Journal of Infectious Diseases | Oxford Academic
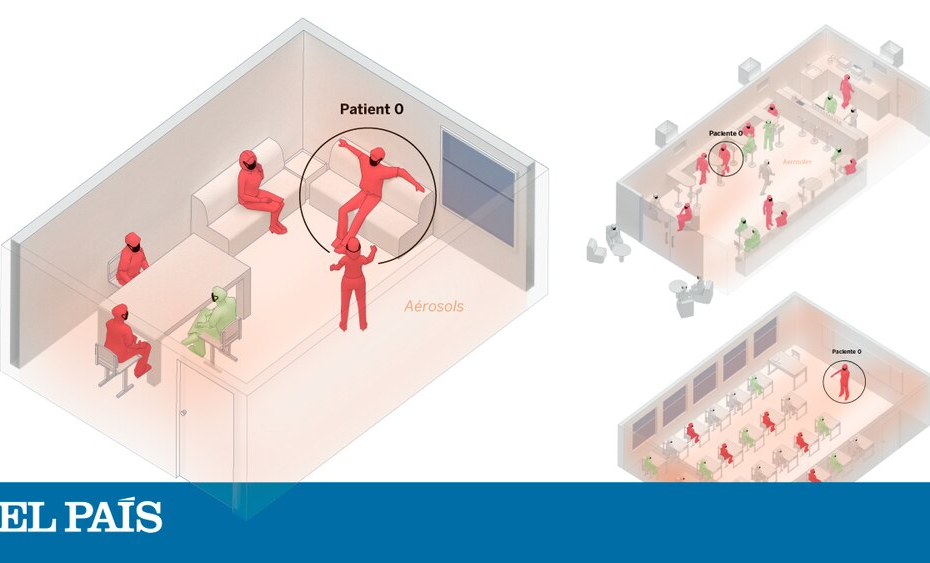
Methods We reviewed published studies/data on detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection in contacts of COVID-19 cases, serological studies, and studies of infections in schools. Results Compared to younger/middle aged adults, susceptibility to infection for children aged under 10y is estimated to be significantly lower, while estimated susceptibility to infection in adults aged over 60y is higher. Serological studies suggest that younger adults (particularly those aged under 35y) often have high cumulative incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the community. There is some evidence that given limited control measures, SARS-CoV-2 may spread robustly in secondary/high schools, and to a lesser degree in primary… Lire la suite »On the effect of age on the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in households, schools and the community | The Journal of Infectious Diseases | Oxford Academic